Turbine oil can be both filtered and purified. In fact, filtration is one of the most common methods used for purification of turbine oil, but the terms "filtering" and "purifying" refer to slightly different processes:
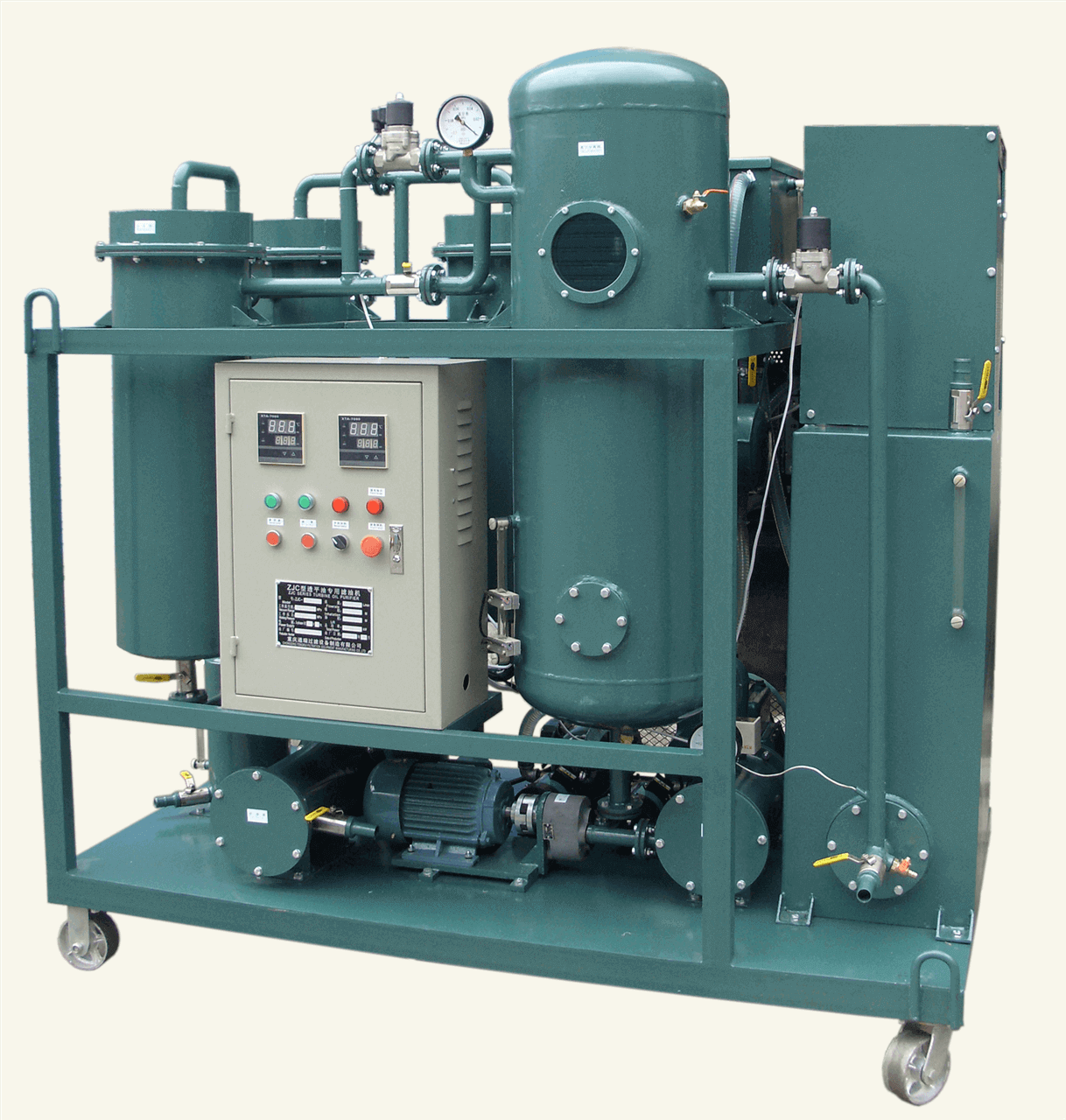
1. Filtration of Turbine Oil
- Filtration is primarily focused on removing solid contaminants from the oil. These contaminants can include dirt, dust, metal wear particles, carbon buildup, or other particulates that can degrade the performance of the turbine system.
- Common types of filters used for turbine oil include:
- Micron filters that catch large particles.
- High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters for fine particulates.
- Depth filters that trap particles within the filter medium.
The filtration process works by passing the oil through a filter material that captures particles based on their size. This method helps to maintain oil cleanliness and protect the turbine components from abrasion and wear.
2. Purification of Turbine Oil
- Purification is a broader concept that not only involves filtering solid contaminants but also removing liquid impurities (e.g., water, gases, oxidation by-products) and chemical contaminants (e.g., acids or sulfur compounds).
Common purification methods include:
- Water Separation: Using coalescers or demulsifiers to remove water from the oil.
- Centrifugation: Using centrifugal force to separate solid and liquid contaminants from the oil.
- Chemical Purification: Using chemicals (e.g., neutralizing agents, antioxidants) to break down harmful contaminants or to stabilize the oil.
- Activated Carbon Adsorption: To remove dissolved organic impurities.
- Ion Exchange: For removing dissolved ions or metals.
- Vacuum Dehydration or Heat Treatment: To remove dissolved gases or free water.
Combining Filtration and Purification
In most cases, turbine oil purification systems incorporate both filtration and additional purification steps to achieve optimal oil cleanliness and quality. A typical oil purification system might:
- Filter out large particles using a coarse filter.
- Use a centrifuge to separate water or solid contaminants.
- Employ a finer filter or adsorption process to capture smaller particles and dissolved impurities.
- Apply chemical treatments or water separation systems to address chemical degradation or moisture contamination.
Benefits of Filtering and Purifying Turbine Oil:
- Improved Performance: Cleaner oil ensures better lubrication, reducing friction and wear in turbine components.
- Longer Oil Life: Regular filtering and purifying reduce the accumulation of contaminants that could lead to oil breakdown, thereby extending oil life.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: By preventing the build-up of harmful particles and water, turbine components stay in better condition, reducing the frequency and cost of maintenance.
- Improved Efficiency: Clean oil allows the turbine to operate more efficiently, reducing energy losses.
Both filtering and purifying turbine oil are essential practices for ensuring that the oil remains free from contaminants that could impair turbine performance and longevity. Filtration is often a component of the overall purification process, but purification goes beyond filtration to address all forms of contamination, including water, gases, and chemical breakdown products.

